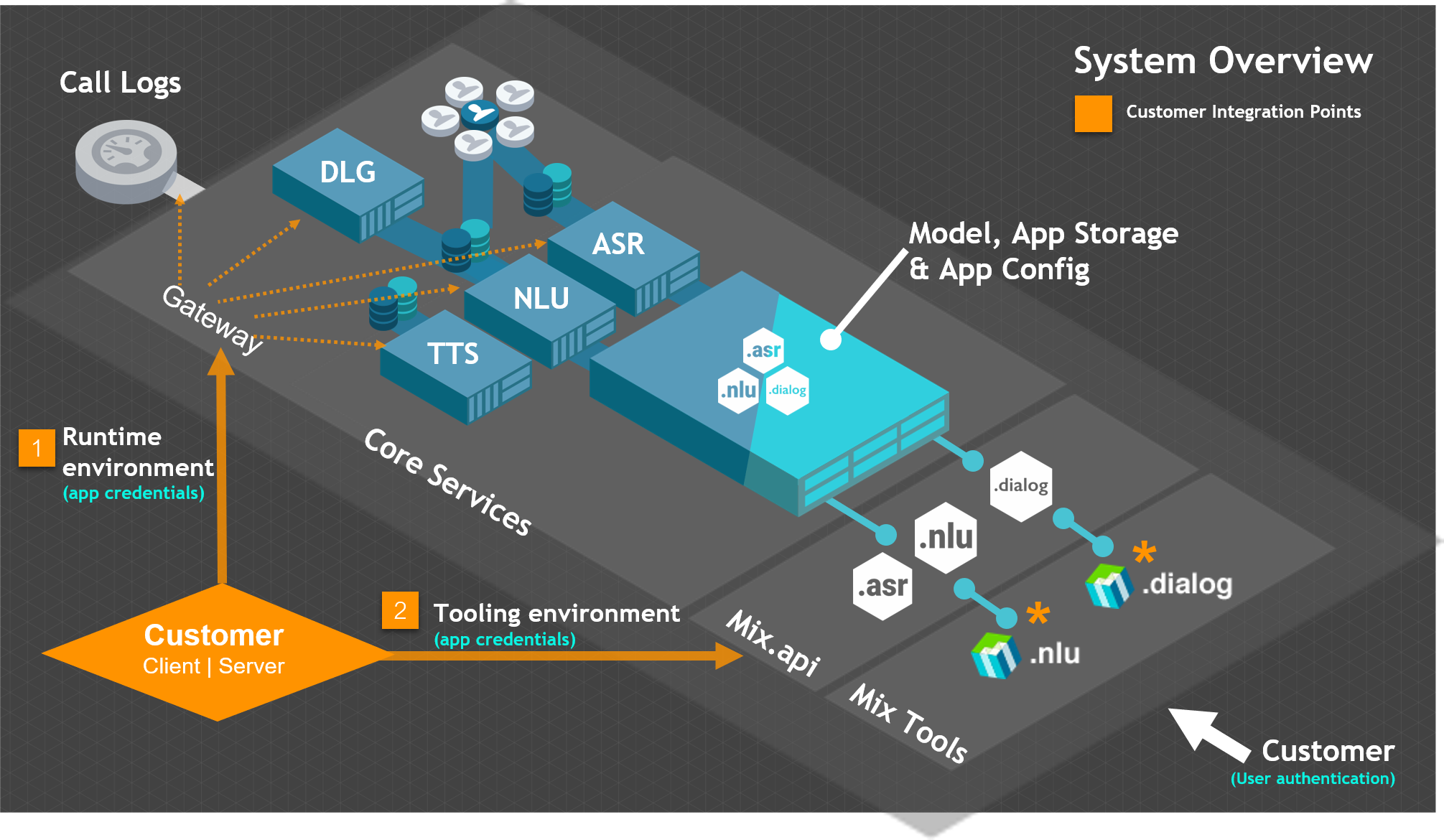
Authorization in Mix
Nuance Mix uses the OAuth 2.0 protocol for authorization. To access the Mix runtime and tooling environments, all client applications must provide a valid access token.
Overview
Authorization process
There are two integration points that require authorization in Mix:
- Runtime environment: To access the ASR, NLU, Dialog, and TTS runtime services as well as runtime logs, applications provide an access token created using client credentials generated from the Mix.dashboard Manage tab.
- Tooling environment: To access the Mix tooling environment, applications provide an access token created using client credentials generated from the Mix.dashboard Profile page.
As per the OAuth 2.0 standard, there are two important concepts related to authorization: Scopes and client credentials.
Scopes
Scope is an OAuth 2.0 mechanism that determines what information the authorized application has access to. In Mix, these scopes are available:
asr: Provides access to the ASRaaS runtime API and resources.nlu: Provides access to the NLUaaS runtime API and resources.dlg: Provides access to the DLGaaS runtime API and resources.tts: Provides access to the TTSaaS runtime API and resources.log: Provides access to call logs.asr.wordset: Allows client applications to upload ASR wordsets.nlu.wordset: Allows client applications to upload NLU wordsets.mix-api: Provides access to the Mix.api endpoints and tooling resources.
Client credentials
Client credentials consist of a client ID and a client secret. The client credentials to use depend on the integration point.
Access to runtime services and logs
To access the runtime services and logs, client applications must provide a valid access token that is created using credentials generated from the Mix.dashboard Manage tab.
These credentials (that is, the client ID and client secret) are linked to an application ID, which identifies an environment in a Mix application. For example, consider the Mix application "My Omni-Channel Application", which has two environments: DEV and PROD:
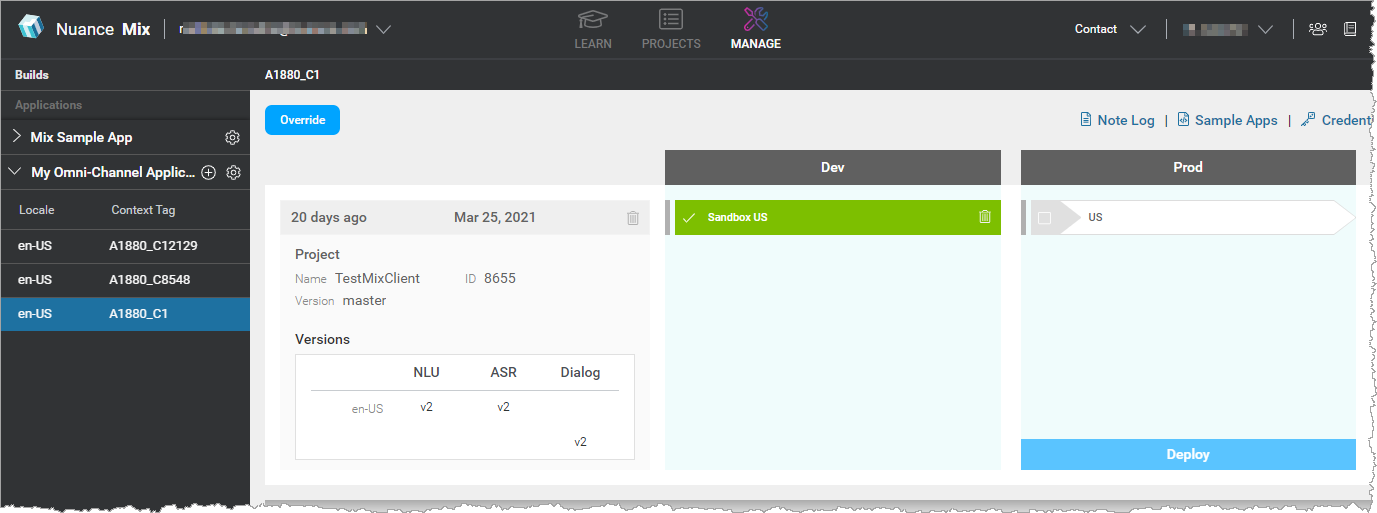
Each environment has its own app ID: DEMO-OMNICHANNEL-APP-DEV and DEMO-OMNICHANNEL-APP-PROD, and each app ID has its own set of client credentials.
Because client credentials are linked to an app ID, they provide access to the resources associated to this app ID.
Client IDs for the runtime environment can use these scopes: asr, nlu, dlg, tts, log, asr.wordset, and nlu.wordset.
The information that the application will have access to depends on the combination of the scope and client ID used to create the access token. For example:
- If an application requests an access token for client ID
appID:DEMO-OMNICHANNEL-APP-PROD:geo:us:clientName:defaultwith scopedlg, this access token will allow the application to use the DLGaaS API and access the resources that were deployed for theDEMO-OMNICHANNEL-APP-PRODapp ID. - If an application requests an access token for client ID
appID:DEMO-OMNICHANNEL-APP-DEV:geo:us:clientName:defaultwith scopelog, this access token will allow the application to use the reporting API and access the call logs for theDEMO-OMNICHANNEL-APP-DEVapp ID.
The runtime services and log use the OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials grant type flow. See Authorize your client application: Runtime for information on creating client credentials and access tokens for the runtime environment.
Access to tooling API (Mix.api)
To access the Mix.api endpoints and tooling resources, client applications must provide an access token that is created using credentials generated from the Mix.dashboard Profile tab.
These credentials (that is, the client ID and client secret) are linked to a user’s account and provide the same permissions of that user.
There are two types of accounts to access the tooling API:
- A user account, which is intended for user-to-service use cases. This account uses the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code grant type flow.
- A service account, which is used for machine identity and is intended for service-to-service use cases. This account uses the OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials grant type flow.
Client IDs created from the Profile tab use the mix-api scope.
See Mix.api authorization for information on creating client credentials and access tokens for the tooling environment.
Summary
This table summarizes the authorization options in Mix:
| Runtime environment | Tooling environment: User account |
Tooling environment: Service account |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| OAuth 2.0 Authorization type | Client Credentials | Authorization Code | Client Credentials |
| Credentials created from | Manage tab | Profile tab | Profile tab |
| Credentials linked to | App ID | User account | User account |
| Supported scopes | asr, nlu, dlg, tts, log, asr.wordset, nlu.wordset |
mix-api |
mix-api |
| Documentation | Authorize your client application: Runtime | Mix.api Authorization Code flow | Mix.api Client Credentials flow |
Authorize your client application: Runtime
Nuance Mix uses the OAuth 2.0 protocol for authorization. All client applications must provide a valid access token to be able to access the ASR, NLU, Dialog, and TTS runtime services as well as the runtime call logs.
In particular, the runtime environment uses the OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials flow, as shown in this diagram:
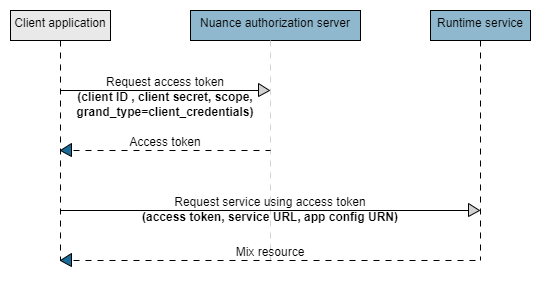
- The client application requests an access token from the Nuance authorization server, providing the client ID and client secret using the HTTP Basic authentication scheme. See Request an access token for an example.
- The Nuance authorization server generates and returns the access token.
- The client application sends a request to one of the Mix runtime services, providing the access token.
- The Mix runtime service authorizes the request by inspecting the access token; if the token is valid, it returns the Mix resource.
To enable authorization in your client application:
- Create a client ID. (Optional; you can use the default client ID if preferred.)
- Generate the client secret for a client ID; the client secret is required to request an access token.
- Request an access token.
- Specify the access token in your client application.
Create a client ID
By default, a single client ID is available for an App ID when you create a project, with a client name of default.
You can create additional client IDs as required.
To create a client ID:
- In Mix.dashboard, click the Manage tab.
- From the menu on the left, select Applications.
- Select the application.
- Click the settings icon
 .
. - Click the App ID tab.
- Click Add a new client.
- In Add a new client, specify a client name and click Create.
The client is added to the App ID tab. For example:
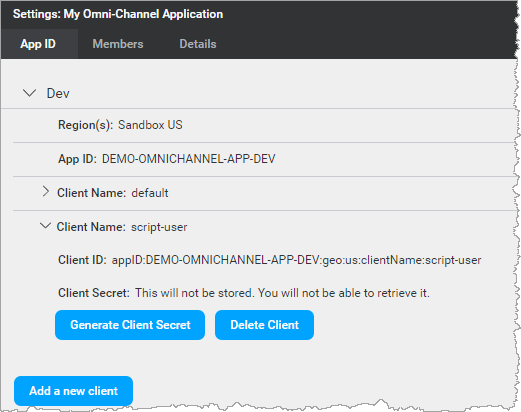
You can now generate the client secret for this client ID and use it to access a runtime service.
Delete a client ID
You can delete client IDs if they are no longer required. Note that you need at least one client ID per App ID.
To delete a client ID:
- In Mix.dashboard, click the Manage tab.
- From the menu on the left, select Applications.
- Select the application.
- Click the settings icon
 .
. - Click the App ID tab.
- Click the arrow beside the client name to show the client details.
- Click Delete Client.
- Click Delete to confirm.
Generate the client secret
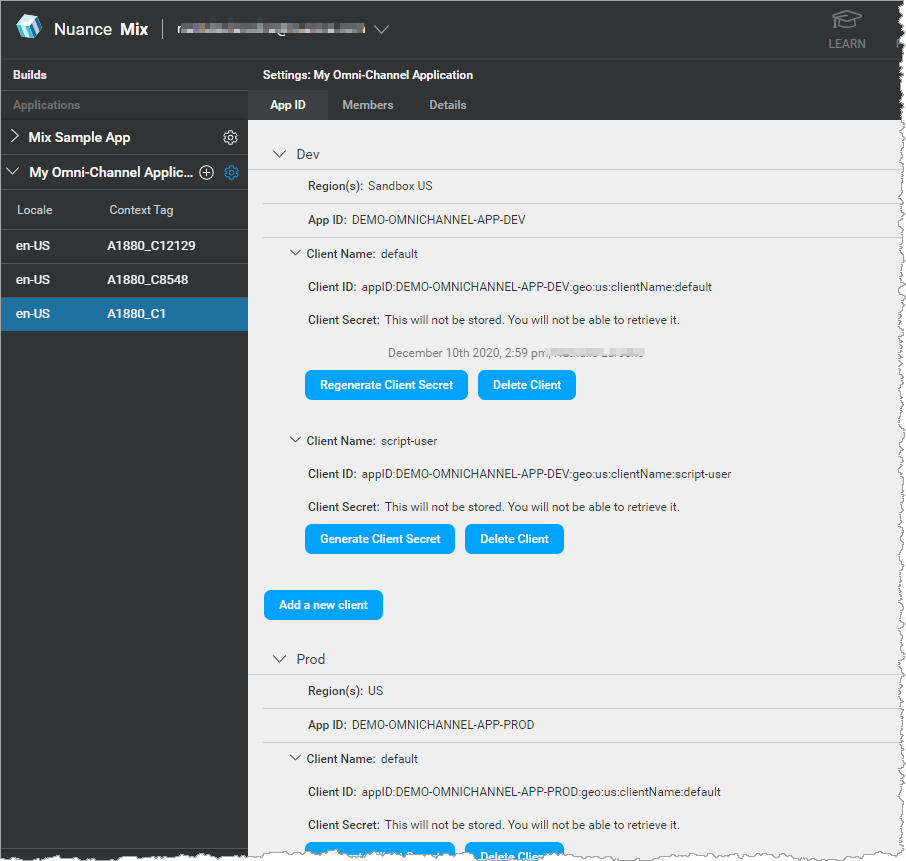
You generate the client secret from the App ID tab. This tab contains this information:
- Region: Region where the application config is deployed.
- App ID: ID for your application.
- One or more Client Names: Clients that can access the runtime services.
For example:

To generate the client secret for a client ID:
- In Mix.dashboard, click the Manage tab.
- From the menu on the left, select Applications.
- Select the application.
- Click the settings icon
 .
. - Click the App ID tab.
- Click the arrow beside the client name to show the client details.
- Click Generate Client Secret.
The client secret is generated.
Note: Only application owners are allowed to generate client secrets.
Specifying the client ID in your application
The client ID is composed of the string appID: followed by a unique ID. When specifying the client ID, you may need to escape the colons in the client ID (that is, :), depending on how you are passing the client ID in your application.
For example, when using the curl command, which already uses a colon in the user option (-u), you need to replace the colon with %3A. For example:
$ export CLIENT_ID="appID%3ANMDPTRIAL_alex_smith_company_com_20190919T190532%3Ageo%3Aqa%3AclientName%3Adefault"
$ export SECRET="riAbk888CC2B.97D7eUklVe6pD"
$ export TOKEN="`curl -s -u "$CLIENT_ID:$SECRET" ...
Regenerate the client secret
You may need to regenerate the client secret for a client ID if, for example, you lose it or if it has become compromised.
To regenerate the client secret:
- In Mix.dashboard, click the Manage tab.
- From the menu on the left, select Applications.
- Select the application.
- Click the settings icon
 .
. - Click the App ID tab.
- Click the arrow beside the client name to show the client details.
- Click Regenerate Client Secret.
- To regenerate the client secret, click "I understand, Regenerate Client Secret."
Request an access token
To request an access token from the Nuance authorization server, you need this information:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
grant_type |
Always set this to client_credentials. |
scope |
Scope for the client credentials grant. Enter one of these scopes:
You can also request a grant for more than one service by separating the scopes with a space. For example, for all the services, specify asr nlu tts dlg; for TTS and Dialog, specify tts dlg. For Mix.api authorization, see Authorization. |
client_id |
Specify the client ID. For example: appID:NMDPTRIAL_alex_smith_company_com_20190919T190532:geo:qa:clientName:default. You can find the client_id in the Credentials tab. See also Specifying the client ID in your application for more information. |
client_secret |
Enter the client secret generated from Mix.dashboard for this client ID. |
| URL of the Nuance authorization server | This is: https://auth.crt.nuance.co.uk/oauth2/token |
When requesting an access token, the Nuance authorization server returns:
- The access token
- The token expiration (provided as the number of seconds after which the token will expire)
- The scope
- The token type (always set to
bearer)
This code shows a sample token request using curl:
Notes:
- The curl command uses python to parse the response received from the Nuance authorization server and extract the token only.
- Note that the colons in the Client_ID are escaped (using
%3Ainstead of:) so that the curl command can be split correctly.
$ export CLIENT_ID="appID%3ANMDPTRIAL_alex_smith_company_com_20190919T190532%3Ageo%3Aqa%3AclientName%3Adefault"
$ export SECRET="riAbk888CC2B.97D7eUklVe6pD"
$ export TOKEN="`curl -s -u "$CLIENT_ID:$SECRET" "https://auth.crt.nuance.co.uk/oauth2/token" -d "grant_type=client_credentials" -d "scope=asr" | python -m json.tool | python -c 'import sys, json; print(json.load(sys.stdin)["access_token"])'`"
Save the token returned in a safe place, as you will need it to access the runtime services.
Access token lifetime
Currently, the access token expires after 15 minutes.
When you receive a token, you also receive the lifespan of the token, in seconds, in the expires_in field. For example:
{"access_token":"eyJhbG*****3UmrGG7ro","expires_in":899,"scope":"dlg",
"token_type":"bearer"}
This is the value that you should use to estimate the validity of the token. As a good practice, Nuance recommends that your client application should:
- Expect that, in rare cases, the token may become invalid or expire before the expected expiration time
- Be able to renew the token and retry the request
Accessing a runtime service
To access a runtime service from your client application, you need this information:
URL of the service
This is the URL of the Mix runtime environment where the application is deployed:
- ASR: asr.api.nuance.co.uk:443
- NLU: nlu.api.nuance.co.uk:443
- Dialog: dlg.api.nuance.co.uk:443
- TTS: tts.api.nuance.co.uk:443
You specify this URL when creating a gRPC channel.
Access token
You specify the token obtained from the Mix access token service as the credentials when creating a gRPC channel.
When using a REST API, specify the access token as a bearer token in the request header.
URN
Mix.asr DLM, Mix.nlu model, and Mix.dialog resource URNs
You specify the URN for the Mix.asr DLM, Mix.nlu model, and Mix.dialog resource to load in your service gRPC API. A URN has this pattern:
urn:nuance-mix:tag:model/context_tag/service(?=language=language)
Where:
- context_tag is the Context Tag specified when creating an application configuration, for example,
A48_C643orcoffee_app - service is one of
mix.asr,mix.nlu, ormix.dialog - language is the Locale of the application configuration. For URNs, this is the 6-letter language code as documented on the Languages page; for example,
eng-USA. This applies to Mix.asr and Mix.nlu only
For example, to load the resource for the American English coffee_app application configuration, specify the URN as follows:
| Service | URN |
|---|---|
| Mix.asr | urn:nuance-mix:tag:model/coffee_app/mix.asr?=language=eng-USA |
| Mix.nlu | urn:nuance-mix:tag:model/coffee_app/mix.nlu?=language=eng-USA |
| Mix.dialog | urn:nuance-mix:tag:model/coffee_app/mix.dialog |
You can find the URN for an application configuration in the Credentials tab.
ASR and NLU wordset URNs
URNs for the ASR and NLU wordsets have one of the following patterns, depending on the level of the wordset:
- Application-level wordset:
urn:nuance-mix:tag:wordset:lang/context_tag/resourceName/language/service - User-level wordset:
urn:nuance-mix:tag:wordset:lang/context_tag/resourceName/lang/service?=user_id=userId
Where:
- context_tag is the context tag name for this wordset. When you create the wordset, you can provide any context tag name. This name does not have to match the context tag of the companion Mix.asr DLM or Mix.nlu model.
- resourceName is the name of the wordset
- service is one of
mix.asrormix.nlu - language is the locale of the wordset. For URNs, this is the 6-letter language code as documented on the Languages page; for example,
eng-USA. - userID is the unique identifier for the user
For example, to upload the Mix.asr cities_wordset application-level wordset, specify the URN as follows:
urn:nuance-mix:tag:wordset:lang/names-places/cities_wordset/eng-USA/mix.asr
For more information about wordsets, see Wordsets in the ASRaaS documentation.
Credentials tab
The information required to access a runtime service is found in the Credentials tab for each deployed application configuration.
To access Credentials:
- In Mix.dashboard, click the Manage tab.
- Click the Applications tab.
- Select the application you want to access.
- On the left panel, select the context tag you want to see credentials for.
- Click Credentials.
The Credentials & IDs for the context tag appear.
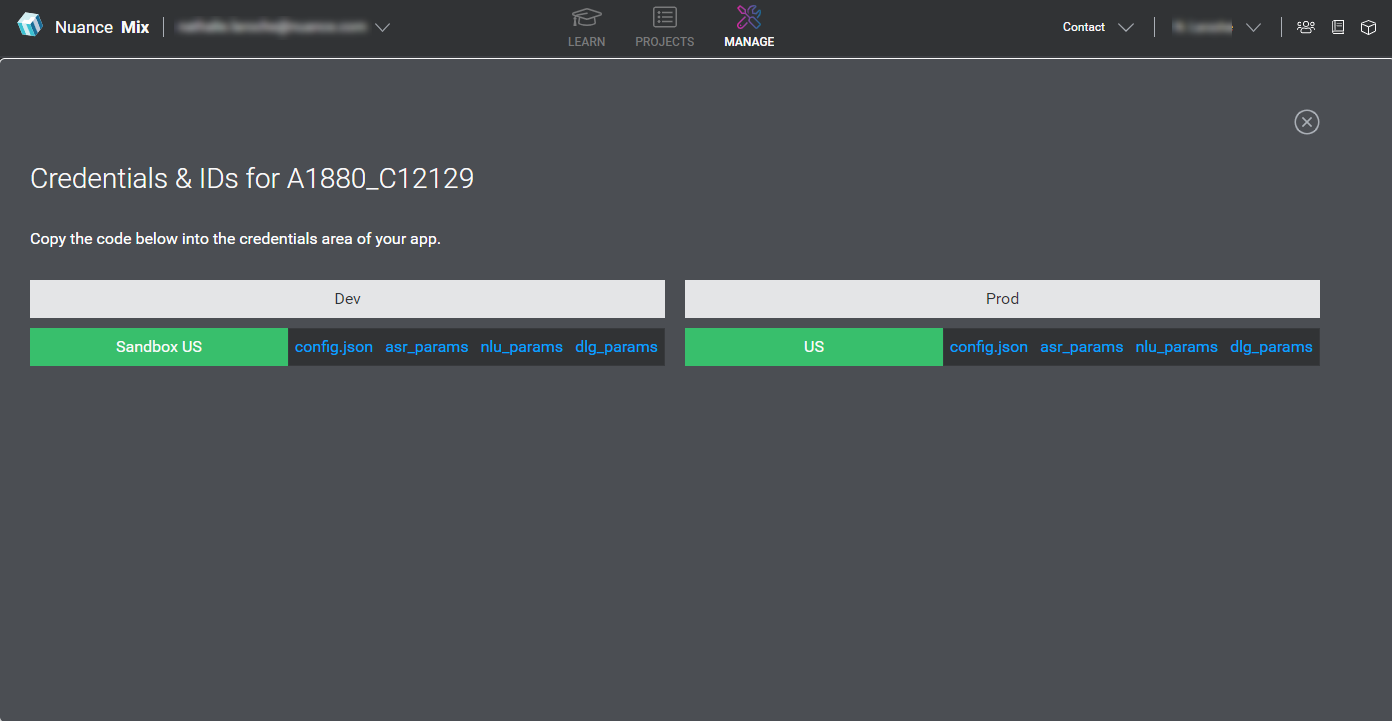
The credentials for each geography are shown under the environment where the application configuration is deployed. Credential blocks are listed to the right of the geography. They include a JSON file to authorize your client application, as well as access parameters for each type of service used by your application configuration.
The credentials listed are specific to an environment geography. For example, credentials for Dev-Sandbox US are different from credentials for Prod US.
The table below summarizes the four types of Credential blocks:
| Credential block | Description |
|---|---|
config.json |
Contains the configuration needed to authorize the client application in the selected environment, in JSON format. |
asr_params |
Contains the URN parameter to access your ASR DLMs application. |
nlu_params |
Contains the URN parameter to access your NLU model application. |
dlg_params |
Contains the URN parameter to access your Dialog application. |
Select each credential block to see the code needed in your client application. You can copy the block by selecting Copy Credential Block.
You can see a sample config.json file below:
{
"client_id": "appID:NMDPTRIAL_colin_birkett_nuance_com_20201005T202248318244:geo:us:clientName:default",
"client_secret": "CLIENT_SECRET", /* to be filled by user */
"oauth_server_url": "https://auth.crt.nuance.co.uk/oauth2/token",
"oauth_scopes": "asr dlg nlu tts log asr.wordset nlu.wordset",
"asr_endpoint": "asr.api.nuance.co.uk:443",
"nlu_endpoint": "nlu.api.nuance.co.uk:443",
"tts_endpoint": "tts.api.nuance.co.uk:443",
"dlg_endpoint": "dlg.api.nuance.co.uk:443"
}
The current parameters for config.json are in the table below:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
client_id |
Provides the client ID needed to access the environment. There can be multiple client IDs. All client IDs defined for an environment geography will be listed in the config.json file. |
client_secret |
A client secret is needed to access the environment geography. See generating the client secret for more information. |
oauth_server_url |
Provides the authorization URL. For example, auth.crt.nuance.co.uk. |
oauth_scopes |
Lists the scopes that are available for the client IDs in this environment geopgraphy. |
asr_endpoint |
Provides the URL of the ASRaaS. |
nlu_endpoint |
Provides the URL of the NLUaaS. |
tts_endpoint |
Provides the URL of the TTSaaS. |
dlg_endpoint |
Provides the URL of the DLGaaS. |